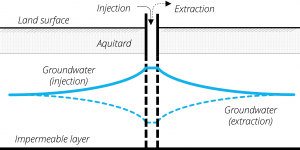
For Aquifer Storage and Recovery (ASR) a constructed deep well is connected to the targeted aquifer and is used for both water extraction and injection. This type of MAR is mainly used where thick and low permeability strata is present above the targeted aquifer. Most currently operating ASR systems store drinking water in the aquifer for recovery in during peak demand or to transfer it from times of high to low availability (e.g. rainy to dry season).
Well injection methods demand a high water quality for the water to be injected as it is directly injected into the aquifer. Overlaying soil strata is of no importance and only little surface area is required for this technology.
| Typical system capacity scale | Village – Town (≈104 m3/year – higher than 106 m3/year). |
| Geology | Confined or unconfined aquifers composed of unconsolidated rocks. |
| Topography | Not relevant for this kind of technology. |
| Soils | Not relevant for this kind of technology. |
| Water source | River water, lake water, storm water, groundwater, etc. High water quality is expected to prevent clogging and pollution of the aquifer. |
| Pre-treatment | High needs for pre-treatment. Water must be treated to prevent clogging and to comply with local groundwater standards. |
| MAR main objective | Recover groundwater levels and to serve as a barrier for saline intrusion. |
| Relative cost | Low-medium. |
Advantages and disadvantages of the system (adapted from IGRAC, 2007):
Advantages
- Clogging is partially remediated during the recovery cycle (water extraction).
- Infiltration of large quantities of water at relatively low cost.
- Non-operative well infrastructure can be used reducing costs. (Wells that had fallen dry)
- Groundwater recharge is not determined by surface characteristics.
Limitations
- Complex design, construction, operation, and maintenance.
- Intensive monitoring of system performance is required.
- High quality source water.
Case studies
- Cocoa Beach Water Reclamation Facility in Cocoa Beach, United States of America
- City of Salisbury, Australia
References
- IGRAC. (2007). Artificial Recharge of Groundwater in the World.
- DEMEAU. (2014). Characterization of European managed aquifer recharge (MAR) sites – Analysis.
