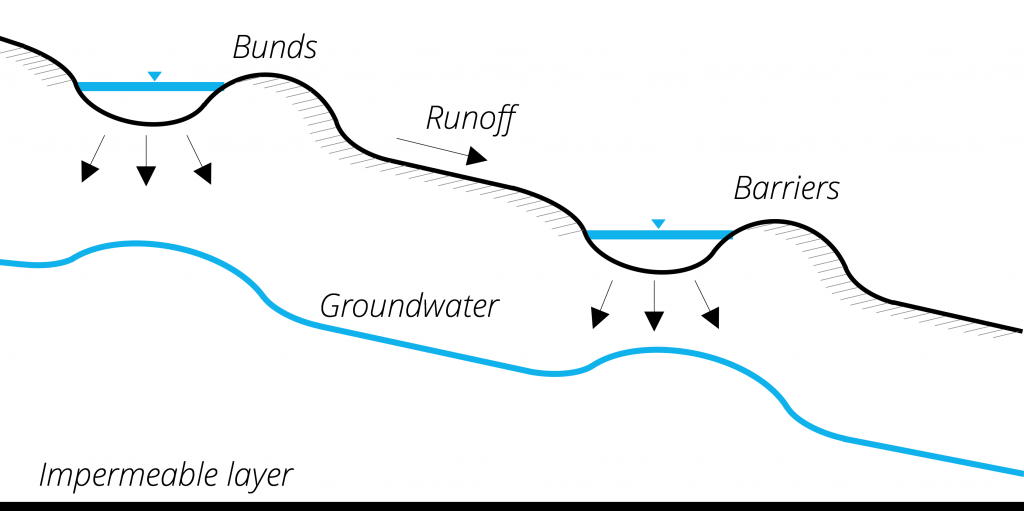
Rainwater harvesting is being increasingly used to collect precipitation water. The ideas of barriers is to obstruct surface runoff from catchments and prohibit flow of the water to be infiltrated. The collected rainwater of rainwater can be achieved by building bunds, barriers or contour ridges. These structures are easy to built and maintain and very adaptable. They can also be used in combination with trenches.
| Typical system capacity scale | Family to Village (10²-10³ m³/a) |
| Geology | Unconfined aquifers. |
| Topography | Rural areas with gently slopes. |
| Soils | Sandy soils. |
| Water source | Rain water. |
| Pre-treatment | None. |
| MAR main objective | Strategic water storage. |
| Cost | Low. |
Advantages and disadvantages of the system (adapted from IGRAC, 2007):
Advantages
- Low cost and simple design.
- Prevention of soil erosion.
Limitations
- Water quality might be problematic (fertilizer).
- Relatively small infiltration quantities.
Case studies
Further information
References
- IGRAC. (2007). Artificial Recharge of Groundwater in the World.
- DEMEAU. (2014). Characterization of European managed aquifer recharge (MAR) sites – Analysis.
